Top 5 Online JavaScript Editors – A Beginner’s Guide
- Posted on
- By Aaron Dumon
- In General,

Online JavaScript editors (JSEs) are invaluable assets for developers of all levels. They streamline coding by allowing you to write JavaScript directly within your web browser, just like you would in a traditional code editor. This flexibility is especially beneficial for beginners and those seeking collaboration with other developers.
With so many JSEs available, choosing the right one can seem daunting. Don’t worry – this article will guide you through the process! We’ll cover:
- Understanding Online JSEs: How do they differ from WYSIWYG HTML editors and full-fledged IDEs (Integrated Development Environments)?
- Benefits of Online JSEs: Explore the advantages they offer, from accessibility to collaboration features.
- Finding the Perfect Fit: Learn how to select an online JavaScript editor that matches your specific needs.
Let’s dive into the world of online JavaScript editing!
What is an online JavaScript editor?
Online JavaScript editors (JSEs) are just what they sound like: browser-based tools for writing, editing, running, and even sharing your JavaScript code. They pack core features found in traditional code editors – syntax highlighting, error checking, and auto-completion – into a convenient online environment. You’ll often find multiple windows within a JSE, dedicated to your HTML, JavaScript, CSS, output, and console.
JSEs and the World of HTML Editors
Understanding JSEs also means knowing a bit about HTML editors. These come in two flavors:
- WYSIWYG Editors: These let you build web content visually, with minimal coding. Think of them as drag-and-drop website builders.
- HTML Code Editors These are text-based, perfect for directly writing HTML and related languages – JavaScript is where JSEs shine!
JSEs vs. IDEs: What’s the Difference?
While both help you build projects, an online JSE is generally more lightweight than a full-fledged IDE (Integrated Development Environment). IDEs are often desktop software with advanced features like in-depth debugging, testing tools, and version control integration.
Related: JS Editor Features
What’s the difference between a JSE and an IDE?
Both JSEs and IDEs have the same goal of making development easier, and they do have their similarities. The main difference between them is that IDEs are much larger tools that consist of a code editor and more. JavaScript editors are typically lightweight and focused on code editing. IDEs, however, also deal with compilation, version control, directory management, testing, and more. Some IDEs even have WYSIWYG functionality within them, letting users write code and use a toolbar for generating components.
Both JavaScript editors and IDEs provide many benefits to users, and neither is better than the other overall. When choosing between the two, you have to assess your needs and what you’re most comfortable with. For instance, if you want to build large applications easily without coding much, then use IDEs or WYSIWYG editors. Similarly, if you’re more comfortable with purely writing code, then JSEs could work.
But for now, we’ll focus on JSEs, specifically the online kind, which are even more lightweight and portable. So, why don’t we explore the benefits that these online editors bring to developers?
Benefits
Here are some of the best benefits that developers can get when using online JavaScript editors:
- Convenience – With online JSEs, developers can access their codes from anywhere provided they have an internet connection. Furthermore, developers won’t have to setup or install anything. This makes prototyping, testing, and helping others with their codes more efficient. That’s why developers also call these editors cloud-based editors.
- Collaboration features – Excellent online JSEs allow multiple developers to work on shared JS codes in real-time. This makes collaboration easier for teams or support groups of developers.
- Versioning – Sometimes, people use online editors once (for something like testing) and never come back. However, there are developers who write large amounts of code using online editors. Luckily for them, some online editors have version tracking, revision history, and version rollback features for smoother maintenance.
- Code sharing – Most online JS editors let their users easily share their code by generating a unique link or embedding it. When you go to Stack Overflow or other developer forums, you’ll see plenty of people sharing their prototype codes.
- Cost-free – One of the best things about editors is that most of them are free. I mean, most HTML code editors are as well, but it’s always nice to have as many free tools as possible, right?
What are the top online JavaScript editors?
I’m sure that you’ve encountered at least one of the top editors we have today. But there are other great ones aside from the most popular editors (you know, the ones we always see on Stack Overflow). Here are the top online JS editors:
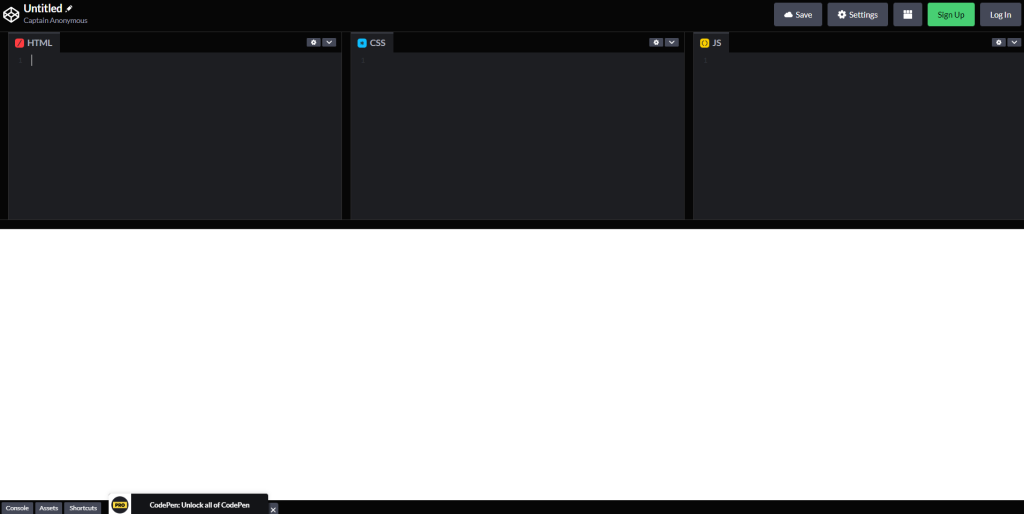
Codepen.io
Codepen is one of the two most popular editors. A “social development environment,” it lets users build, deploy, test, and share their work. It has a clean interface, which by default shows the HTML, CSS, and JS windows separately, with the output and console below. It has the following features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Autocomplete
- Theming and font styling
- Various editor options (format on save, line numbers, etc.)
- Support for customizable code embedding
- Drag-and-drop asset hosting
- Project directory management (IDE-like experience)
- Real-time collaboration
- Private codes with access control
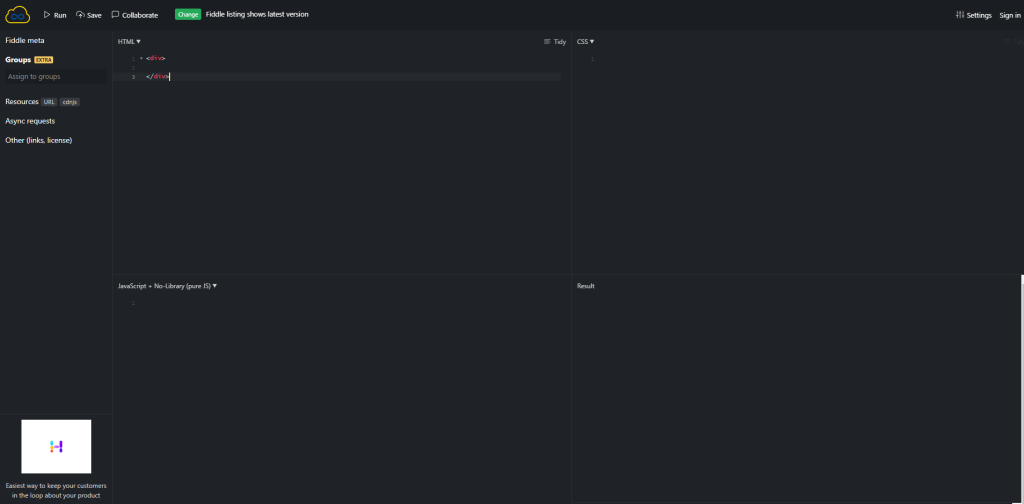
JSFiddle
JSFiddle is another highly popular online JS editor. It’s simple, lightweight, and intuitive. It has four windows (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and result with console). JSFiddle also supports frameworks like Vue, libraries like React, and even similar languages like TypeScript. Here are some of its features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Autocomplete
- Theming
- Various editor options (line numbers, auto-run code, etc.)
- Different available window layouts
- Import resources
- Asynchronous requests simulation
- Real-time collaboration
- Private codes with access control
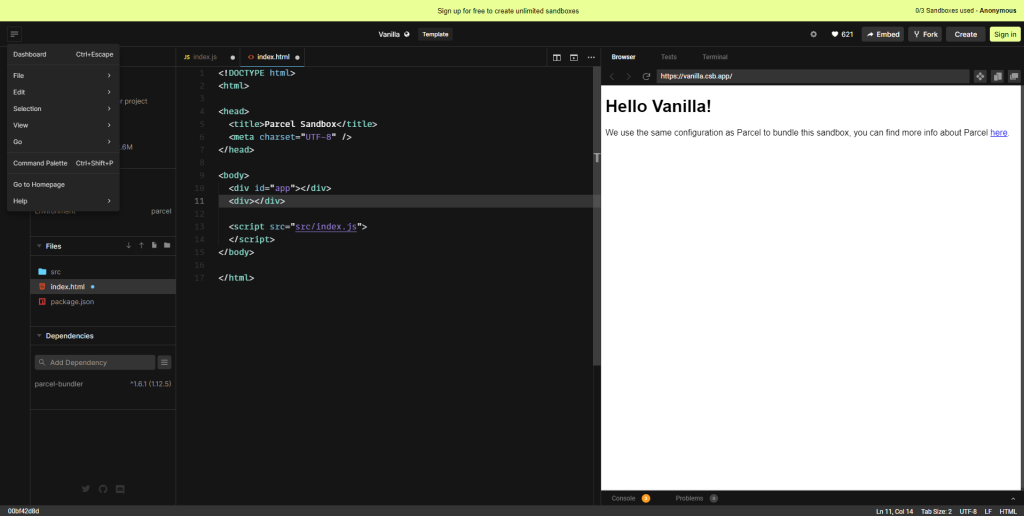
CodeSandbox
CodeSandbox is another heavyweight online JavaScript editor when it comes to features. It promises to supercharge developers’ workflows with its cloud development capabilities. It also supports frameworks and libraries like Angular, React, and more. Here are some of the things it can do:
- Syntax highlighting
- Autocomplete
- Templates
- Import from GitHub
- A modern browser-like results window
- Support for testing
- Project directory management
- Real-time collaboration
- Private codes with access control
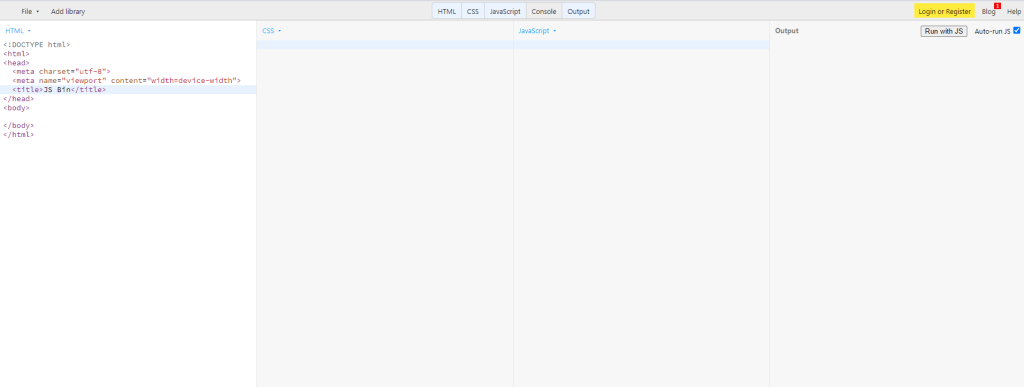
JS Bin
JSBin is a simple yet handy. It might not look as great as the others, and it might not have a lot of features, but it’s perfect for simple tests. Aside from HTML, it also supports Markdown and conversion to HTML. Here are its capabilities:
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto-run code
- Export as gist (Git repository)
- Save as template
- Easy inclusion of JS libraries and frameworks
- Private codes with access control
W3Schools online editor
When developers start their web coding journey, they will probably visit W3Schools at some point. What’s good about the site, aside from its tutorials, is that it has a built-in online editor. Unlike the other editors on this list, its online editor is primarily focused on learning. Thus, it’s more lightweight; however, it’s on this list because of its usefulness to beginners and experienced developers alike. Its features include:
- Syntax highlighting
- Basic theming
- Basic layout choices (portrait or landscape)
- Code saving
Ideal features of an editor
Choosing an online JSE involves the same steps as choosing any other helpful tool. You should assess your requirements, check the editors’ features, and then check their pricing. Usually, the free features can handle most development or testing needs. At the very least, you should ensure that the editor has syntax highlighting. If you’ll use it for your business or to test out confidential codes, then you can try those with the private codes feature.
How to run code in an online JSE
Running code takes very little time in online JavaScript editors. Once you have your code ready, you should click the run, save, or play button (depending on how the editor calls it). Afterwards, the editor will run the code and produce the output in the result window. If the code has any errors, the editor will display them on the console. Some editors also have an auto-run feature.
Conclusion
The online JavaScript editor tool has blessed developers with its convenience since its introduction. And these tools are likely to stay because of that. In fact, they’re getting better with each passing year. As developers, we have to improve productivity with JSE and other tools. In this article, we talked about the top five online JS editors. Always remember that the best among them is the one that fits your project the most.
Aaron Dumon
Aaron Dumona former writer for Froala, showcased exceptional talent and dedication during their tenure with the company.
-
Hide Show






No comment yet, add your voice below!